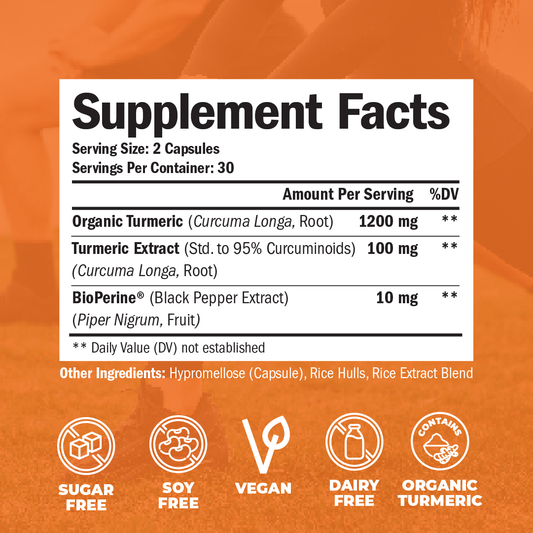
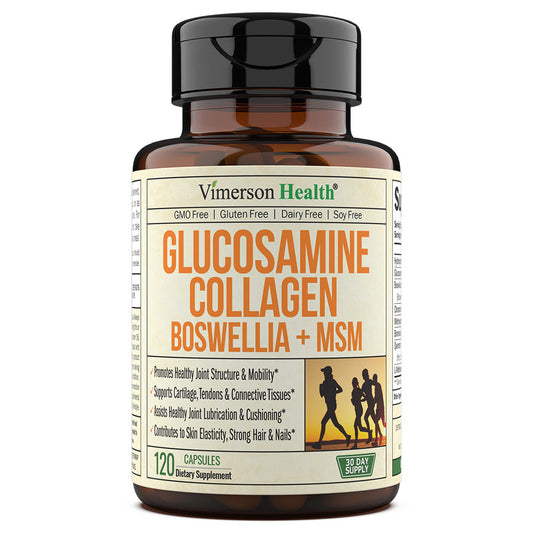
WHAT CAUSES JOINT PAIN ALL OVER THE BODY?
Dive into our comprehensive guide on understanding and managing joint pain, a condition affecting millions worldwide. This detailed article explores the myriad causes of joint discomfort, from arthritis and injury to inflammation and lifestyle factors. Discover effective treatments, natural remedies, and proactive strategies for alleviating pain and improving joint health. Uncover the keys to mitigating joint pain and embracing a more active, pain-free life!